基础图形绘制-圆
中点画圆
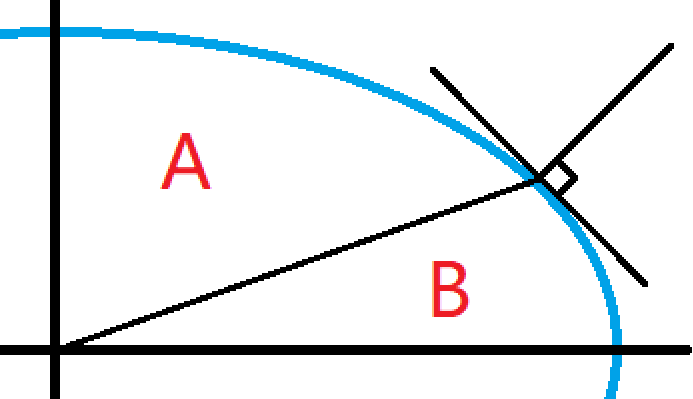
首先,我们考虑画圆心在 ( 0 , 0 ) (0,0) ( 0 , 0 )
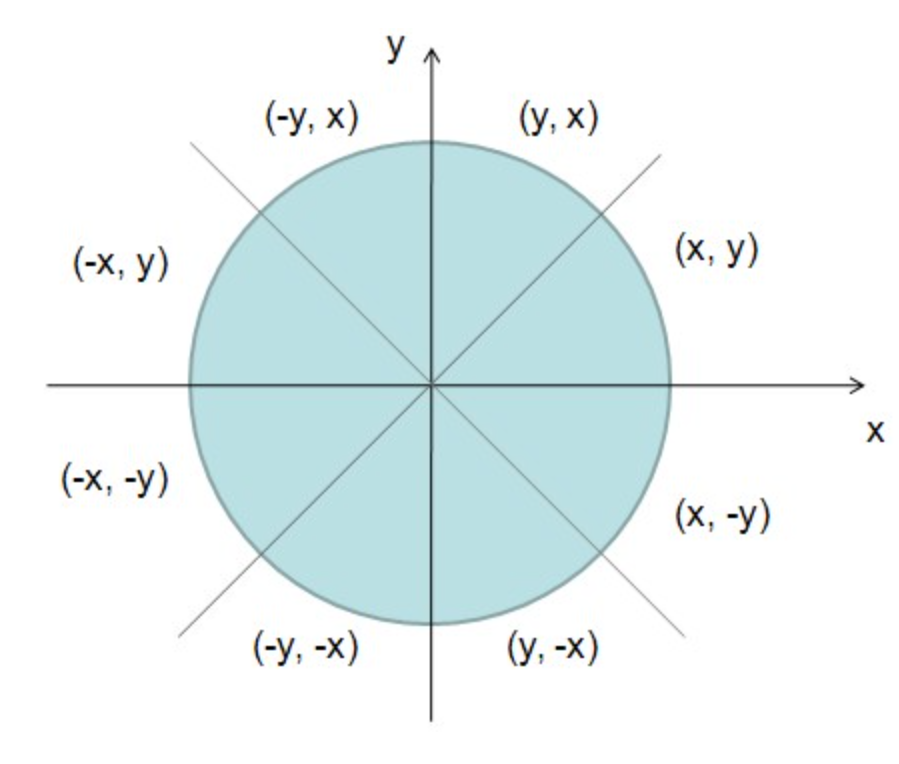
根据圆的对称性,我们只需要画出第一象限的 1 8 \frac{1}{8} 8 1
圆心在 ( 0 , 0 ) (0,0) ( 0 , 0 ) R R R F ( x , y ) = x 2 + y 2 − R 2 = 0 F(x,y)=x^2+y^2-R^2=0 F ( x , y ) = x 2 + y 2 − R 2 = 0
当 F ( x , y ) = x 2 + y 2 − R 2 = 0 F(x,y)=x^2+y^2-R^2=0 F ( x , y ) = x 2 + y 2 − R 2 = 0
当 F ( x , y ) = x 2 + y 2 − R 2 > 0 F(x,y)=x^2+y^2-R^2 \gt 0 F ( x , y ) = x 2 + y 2 − R 2 > 0
当 F ( x , y ) = x 2 + y 2 − R 2 < 0 F(x,y)=x^2+y^2-R^2 \lt 0 F ( x , y ) = x 2 + y 2 − R 2 < 0
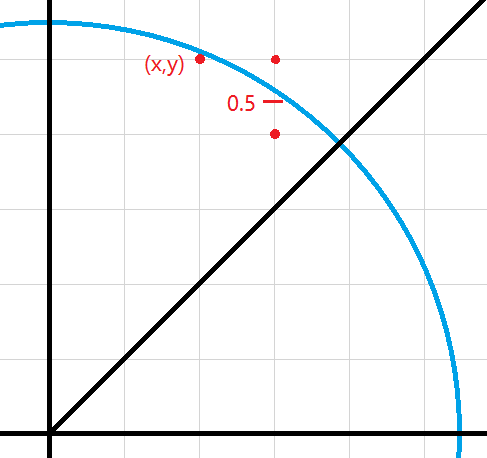
考虑画右上方的 1 8 \frac{1}{8} 8 1 ( x , y ) (x,y) ( x , y ) ( x + 1 , y ) (x+1,y) ( x + 1 , y ) ( x + 1 , y − 1 ) (x+1,y-1) ( x + 1 , y − 1 )
下一个点显然是选择 离圆弧更近的点 ,我们可以通过判断 ( x + 1 , y − 0.5 ) (x+1,y-0.5) ( x + 1 , y − 0.5 ) 圆内 还是 圆外 ,来判断 ( x + 1 , y ) (x+1,y) ( x + 1 , y ) ( x + 1 , y − 1 ) (x+1,y-1) ( x + 1 , y − 1 ) ( x + 1 , y − 0.5 ) (x+1,y-0.5) ( x + 1 , y − 0.5 ) 恰好在圆上 ,算法选择 ( x + 1 , y − 1 ) (x+1,y-1) ( x + 1 , y − 1 )
也就是说,对于 ( x , y ) (x,y) ( x , y )
d = F ( x + 1 , y − 0.5 ) = ( x + 1 ) 2 + ( y − 0.5 ) 2 − R 2 = x 2 + y 2 + 2 x − y + 1.25 − R 2 \begin{aligned}
d &= F(x+1,y-0.5)\\
&= (x+1)^2+(y-0.5)^2-R^2\\
&= x^2+y^2+2x-y+1.25-R^2
\end{aligned}
d = F ( x + 1 , y − 0.5 ) = ( x + 1 ) 2 + ( y − 0.5 ) 2 − R 2 = x 2 + y 2 + 2 x − y + 1.25 − R 2
的值,来判断下一个点的选择情况。
若 d < 0 d \lt 0 d < 0 ( x + 1 , y ) (x+1,y) ( x + 1 , y ) ( x + 1 , y ) (x+1,y) ( x + 1 , y )
d ′ = F ( ( x + 1 ) + 1 , ( y ) − 0.5 ) = F ( x + 2 , y − 0.5 ) = ( x + 2 ) 2 + ( y − 0.5 ) 2 − R 2 = x 2 + y 2 + 4 x − y + 4.25 − R 2 = ( x 2 + y 2 + 2 x − y + 1.25 − R 2 ) + 2 x + 3 = d + 2 x + 3 \begin{aligned}
d' &= F((x+1)+1,(y)-0.5)\\
&= F(x+2,y-0.5)\\
&= (x+2)^2+(y-0.5)^2-R^2\\
&= x^2+y^2+4x-y+4.25-R^2\\
&= (x^2+y^2+2x-y+1.25-R^2)+2x+3\\
&= d+2x+3
\end{aligned}
d ′ = F (( x + 1 ) + 1 , ( y ) − 0.5 ) = F ( x + 2 , y − 0.5 ) = ( x + 2 ) 2 + ( y − 0.5 ) 2 − R 2 = x 2 + y 2 + 4 x − y + 4.25 − R 2 = ( x 2 + y 2 + 2 x − y + 1.25 − R 2 ) + 2 x + 3 = d + 2 x + 3
若 d ≥ 0 d \ge 0 d ≥ 0 ( x + 1 , y − 1 ) (x+1,y-1) ( x + 1 , y − 1 ) ( x + 1 , y − 1 ) (x+1,y-1) ( x + 1 , y − 1 )
d ′ = F ( ( x + 1 ) + 1 , ( y − 1 ) − 0.5 ) = F ( x + 2 , y − 1.5 ) = ( x + 2 ) 2 + ( y − 1.5 ) 2 − R 2 = x 2 + y 2 + 4 x − 3 y + 6.25 − R 2 = ( x 2 + y 2 + 2 x − y + 1.25 − R 2 ) + 2 x − 2 y + 5 = d + 2 x − 2 y + 5 \begin{aligned}
d' &= F((x+1)+1,(y-1)-0.5)\\
&= F(x+2,y-1.5)\\
&= (x+2)^2+(y-1.5)^2-R^2\\
&= x^2+y^2+4x-3y+6.25-R^2\\
&= (x^2+y^2+2x-y+1.25-R^2)+2x-2y+5\\
&= d+2x-2y+5
\end{aligned}
d ′ = F (( x + 1 ) + 1 , ( y − 1 ) − 0.5 ) = F ( x + 2 , y − 1.5 ) = ( x + 2 ) 2 + ( y − 1.5 ) 2 − R 2 = x 2 + y 2 + 4 x − 3 y + 6.25 − R 2 = ( x 2 + y 2 + 2 x − y + 1.25 − R 2 ) + 2 x − 2 y + 5 = d + 2 x − 2 y + 5
这样我们就可以递推 d d d
同时考虑初始点 ( 0 , R ) (0,R) ( 0 , R )
d 0 = F ( 0 + 1 , R − 0.5 ) = 1 + ( R − 0.5 ) 2 − R 2 = 1.25 − R \begin{aligned}
d_0 &= F(0+1,R-0.5)\\
&= 1+(R-0.5)^2-R^2\\
&= 1.25-R
\end{aligned}
d 0 = F ( 0 + 1 , R − 0.5 ) = 1 + ( R − 0.5 ) 2 − R 2 = 1.25 − R
这样,我们就可以画出基础的圆。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 static int dx[] = { 1 , 1 , -1 , -1 };static int dy[] = { 1 , -1 , 1 , -1 };static void Normalize (float & x, float & y) x = (x - (SCR_WIDTH / 2 )) / (SCR_WIDTH / 2 ); y = (y - (SCR_HEIGHT / 2 )) / (SCR_HEIGHT / 2 ); } static void MiddlePoint (int x0, int y0, int R) int x = 0 , y = R; double d = 1.25 - R; while (x < y) { if (d < 0 ) d = d + 2 * x + 3 ; else y--, d = d + 2 * x - 2 * y + 5 ; x++; for (int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++) { vertices[count * 3 ] = x * dx[i] + x0, vertices[count * 3 + 1 ] = y * dy[i] + y0; Normalize (vertices[count * 3 ], vertices[count * 3 + 1 ]), count++; vertices[count * 3 ] = y * dx[i] + x0, vertices[count * 3 + 1 ] = x * dy[i] + y0; Normalize (vertices[count * 3 ], vertices[count * 3 + 1 ]), count++; } } }
Bresenham
Bresenham 算法是对 中点画圆 算法的改进。
我们发现 中点画圆 算法中 d d d Bresenham 算法:
我们先将所有的关于 d d d d = 2 × ( 1.25 − R ) = 2.5 − 2 R d=2 \times (1.25-R) =2.5-2R d = 2 × ( 1.25 − R ) = 2.5 − 2 R 3 − 2 R 3-2R 3 − 2 R
d d d 3 − 2 R 3-2R 3 − 2 R d < 0 d \lt 0 d < 0 d ′ = d + 4 x + 6 d'=d+4x+6 d ′ = d + 4 x + 6 d ≥ 0 d \ge 0 d ≥ 0 d ′ = d + 4 x − 4 y + 10 d'=d+4x-4y+10 d ′ = d + 4 x − 4 y + 10
可以发现效果较好的同时消除了浮点运算。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 static int dx[] = { 1 , 1 , -1 , -1 };static int dy[] = { 1 , -1 , 1 , -1 };static void Normalize (float & x, float & y) x = (x - (SCR_WIDTH / 2 )) / (SCR_WIDTH / 2 ); y = (y - (SCR_HEIGHT / 2 )) / (SCR_HEIGHT / 2 ); } static void Bresenham (int x0, int y0, int R) int x = 0 , y = R, d = 3 - 2 * R; while (x < y) { if (d < 0 ) d = d + 4 * x + 6 ; else y--, d = d + 4 * x - 4 * y + 10 ; x++; for (int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++) { vertices[count * 3 ] = x * dx[i] + x0, vertices[count * 3 + 1 ] = y * dy[i] + y0; Normalize (vertices[count * 3 ], vertices[count * 3 + 1 ]), count++; vertices[count * 3 ] = y * dx[i] + x0, vertices[count * 3 + 1 ] = x * dy[i] + y0; Normalize (vertices[count * 3 ], vertices[count * 3 + 1 ]), count++; } } }
OpenGL 完整代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 #define GLEW_STATIC #include <GL/glew.h> #include <GL/GL.h> #include <GLFW/glfw3.h> #include <iostream> #pragma region Setting static GLFWwindow* window;const unsigned int SCR_WIDTH = 800 ;const unsigned int SCR_HEIGHT = 600 ;const unsigned int MAX_COUNT = 800 * 600 ;static void InitializeWindow () glfwInit (); glfwWindowHint (GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MAJOR, 3 ); glfwWindowHint (GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MINOR, 3 ); glfwWindowHint (GLFW_OPENGL_PROFILE, GLFW_OPENGL_CORE_PROFILE); window = glfwCreateWindow (SCR_WIDTH, SCR_HEIGHT, "Test" , NULL , NULL ); glfwMakeContextCurrent (window); glfwSetFramebufferSizeCallback (window, [](GLFWwindow* window, int width, int height){ glViewport (0 , 0 , width, height); }); glewExperimental = GL_TRUE; glewInit (); } static void ProcessInput (GLFWwindow* window) if (glfwGetKey (window, GLFW_KEY_ESCAPE) == GLFW_PRESS) glfwSetWindowShouldClose (window, true ); } #pragma endregion #pragma region InitializeVertex static float vertices[MAX_COUNT * 3 ];static unsigned int VAO, VBO;static unsigned int count = 0 ;static int dx[] = { 1 , 1 , -1 , -1 };static int dy[] = { 1 , -1 , 1 , -1 };static void Normalize (float & x, float & y) x = (x - (SCR_WIDTH / 2 )) / (SCR_WIDTH / 2 ); y = (y - (SCR_HEIGHT / 2 )) / (SCR_HEIGHT / 2 ); } static void MiddlePoint (int x0, int y0, int R) int x = 0 , y = R, d = 1.25 - R; while (x < y) { if (d < 0 ) d = d + 2 * x + 3 ; else y--, d = d + 2 * x - 2 * y + 5 ; x++; for (int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++) { vertices[count * 3 ] = x * dx[i] + x0, vertices[count * 3 + 1 ] = y * dy[i] + y0; Normalize (vertices[count * 3 ], vertices[count * 3 + 1 ]), count++; vertices[count * 3 ] = y * dx[i] + x0, vertices[count * 3 + 1 ] = x * dy[i] + y0; Normalize (vertices[count * 3 ], vertices[count * 3 + 1 ]), count++; } } } static void Bresenham (int x0, int y0, int R) int x = 0 , y = R, d = 3 - 2 * R; while (x < y) { if (d < 0 ) d = d + 4 * x + 6 ; else y--, d = d + 4 * x - 4 * y + 10 ; x++; for (int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++) { vertices[count * 3 ] = x * dx[i] + x0, vertices[count * 3 + 1 ] = y * dy[i] + y0; Normalize (vertices[count * 3 ], vertices[count * 3 + 1 ]), count++; vertices[count * 3 ] = y * dx[i] + x0, vertices[count * 3 + 1 ] = x * dy[i] + y0; Normalize (vertices[count * 3 ], vertices[count * 3 + 1 ]), count++; } } } static void InitializeVertex () glGenVertexArrays (1 , &VAO); glGenBuffers (1 , &VBO); glBindVertexArray (VAO); glBindBuffer (GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, VBO); glBufferData (GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof glVertexAttribPointer (0 , 3 , GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 3 * sizeof float ), (void *)0 ); glEnableVertexAttribArray (0 ); } #pragma endregion void Render () glClearColor (0.5 , 0.5 , 0.5 , 1 ); glClear (GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT); glBindVertexArray (VAO); glDrawArrays (GL_POINTS, 0 , count); } int main () int x0, y0, R; std::cin >> x0 >> y0 >> R; InitializeWindow (); MiddlePoint (x0, y0, R); Bresenham (x0, y0, R); InitializeVertex (); while (!glfwWindowShouldClose (window)) { ProcessInput (window); Render (); glfwSwapBuffers (window); glfwPollEvents (); } glfwTerminate (); return 0 ; }